Cloud app operations
Categories:
Prior reading: Cloud apps overview
Purpose: This document provides detailed instructions for performing operations on cloud apps through the Verily Workbench web UI.
Notes: These instructions all assume that you have already opened a workspace in the Workbench web UI and navigated to the Apps tab. This document does not cover doing work within a cloud app, nor installing additional libraries/software.
Vertex AI-based Jupyterlab apps are going away soon
We've added support for Compute Engine as an alternative. After Jan. 30, 2025, existing Vertex AI-based apps will keep working, but the ability to create new ones will be removed. To learn more, see Introducing the Workbench JupyterLab app.List your cloud apps and check their status
Your apps are listed in the Apps tab of the workspace.
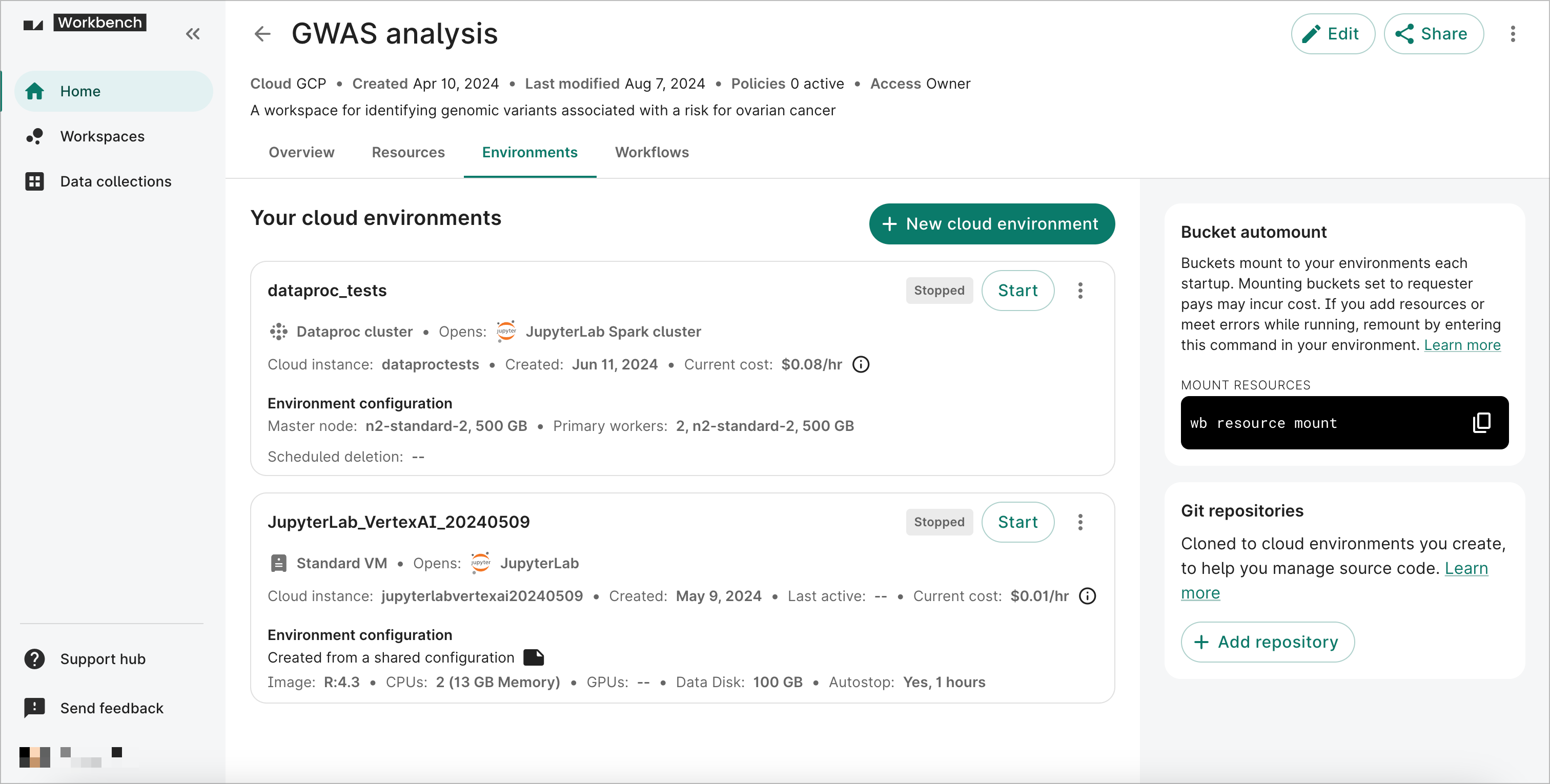
A badge in the top right corner of each app's card denotes its status, which can be one of the following:
- Creating
- Provisioning
- Startup script
- Starting
- Running
- Stopping
- Stopped
For more information about the operations you can perform on apps that are either Stopped or Running, see Operations on existing apps. Apps that are in the process of Starting or Stopping cannot be operated on.
If you have an app that seems stuck on either Starting or Stopping, please contact the support team for help.
Create a new cloud app (JupyterLab Vertex AI Workbench instance)
In the Apps tab of your workspace:
-
Click New app instance to open the Creating app dialog.
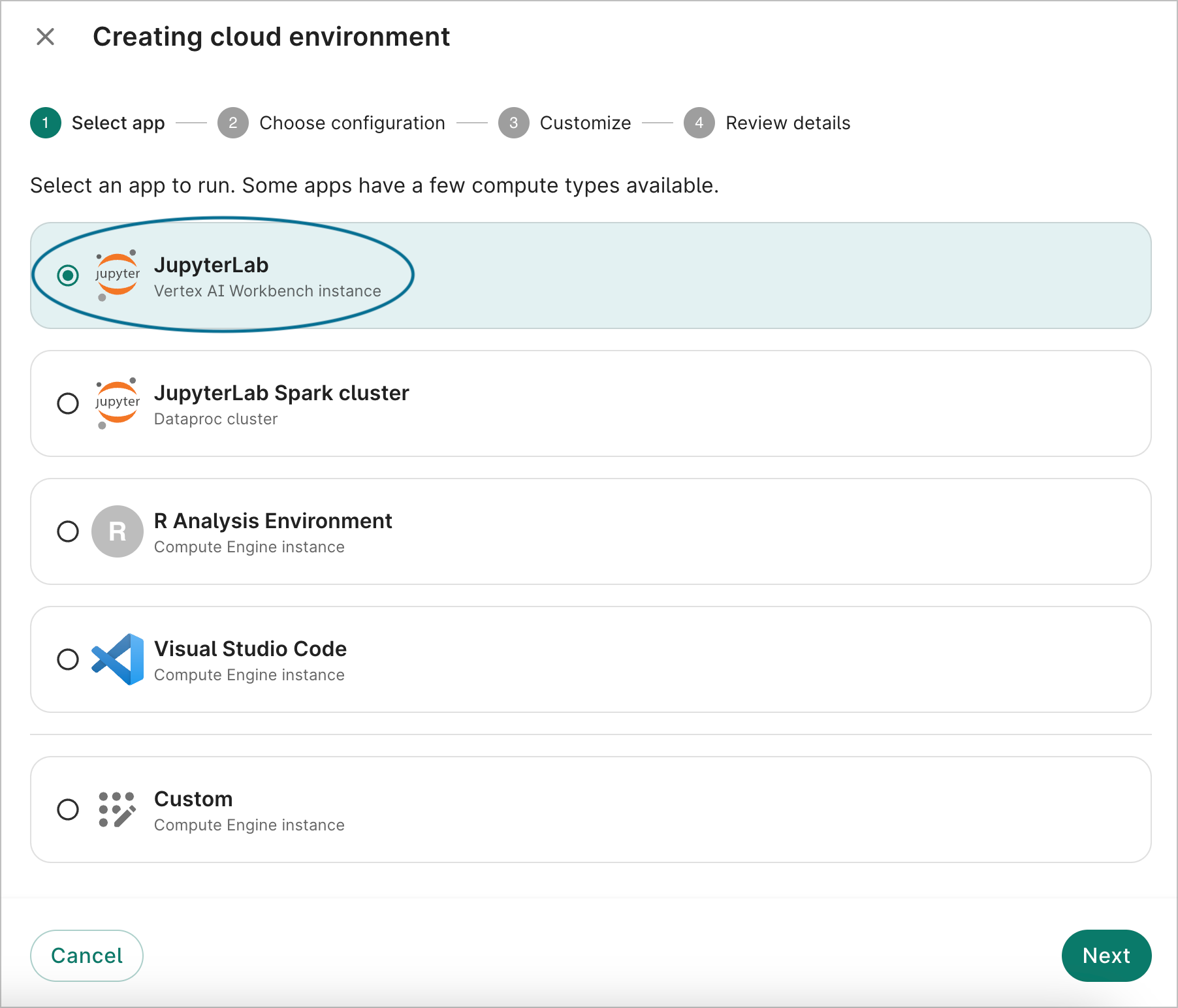
-
Either select an app from the list, or select the custom Compute Engine instance option. In the image below, the JupyterLab Vertex AI Workbench instance is selected. Click the Next button.
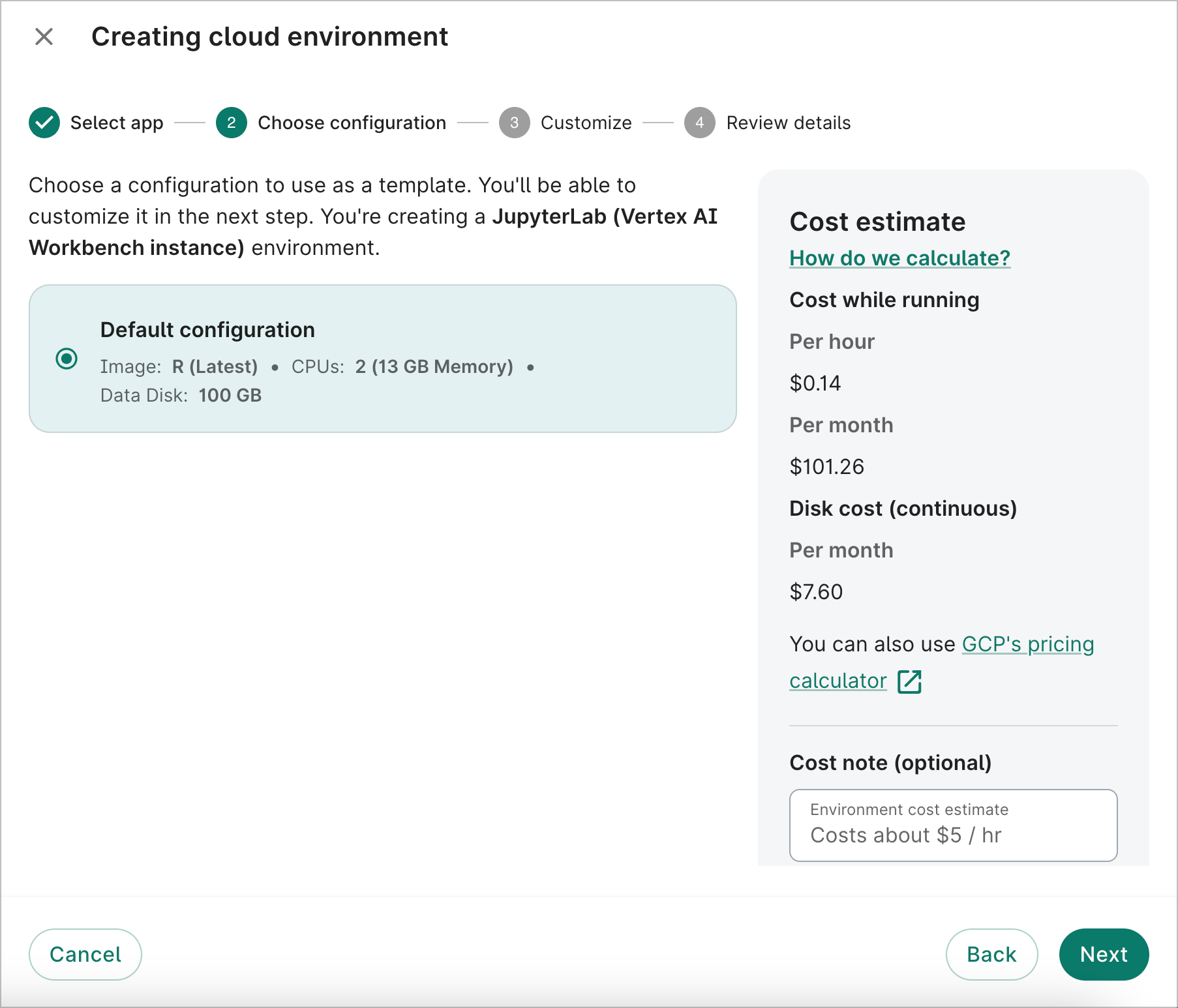
-
A default configuration will already be selected for you. Click the Next button.
-
Select an app image, or enter a custom container. In the image below, the TensorFlow Enterprise image is selected.
You can also change the number of CPUs, which in turn changes the total memory available. If you selected a PyTorch or TensorFlow Enterprise image, you can also attach GPUs to the VM.
In addition, you can change the data disk size for your app. The default recommended size is 100 GB for Vertex AI Workbench instances and 500 GB for Compute Engine instances. However, it can range from 10 GB to 64,000 GB (64 TB). Please note that the data disk size can't currently be customized via the UI for Dataproc clusters.
Tip
It's possible to create notebooks from other Deep Learning VM apps as well, via the Workbench CLI. See Choose an image for more information on specifying image versions. You can run a command like the following (substituting your notebook name, and specifying machine type, accelerators, etc. as desired):
wb resource create gcp-notebook \
--id <your-notebook-name> \
--machine-type=<MACHINE_TYPE> \
--location=us-central1-a \
--vm-image-family=<IMAGE_FAMILY> \
--vm-image-project=deeplearning-platform-release
Finally, you can choose to have a running app automatically stop after a specified idle time. The autostop idle time is set to 4 hours by default, but it can range from 1 hour to 14 days. You can also choose to opt out of the autostop feature.
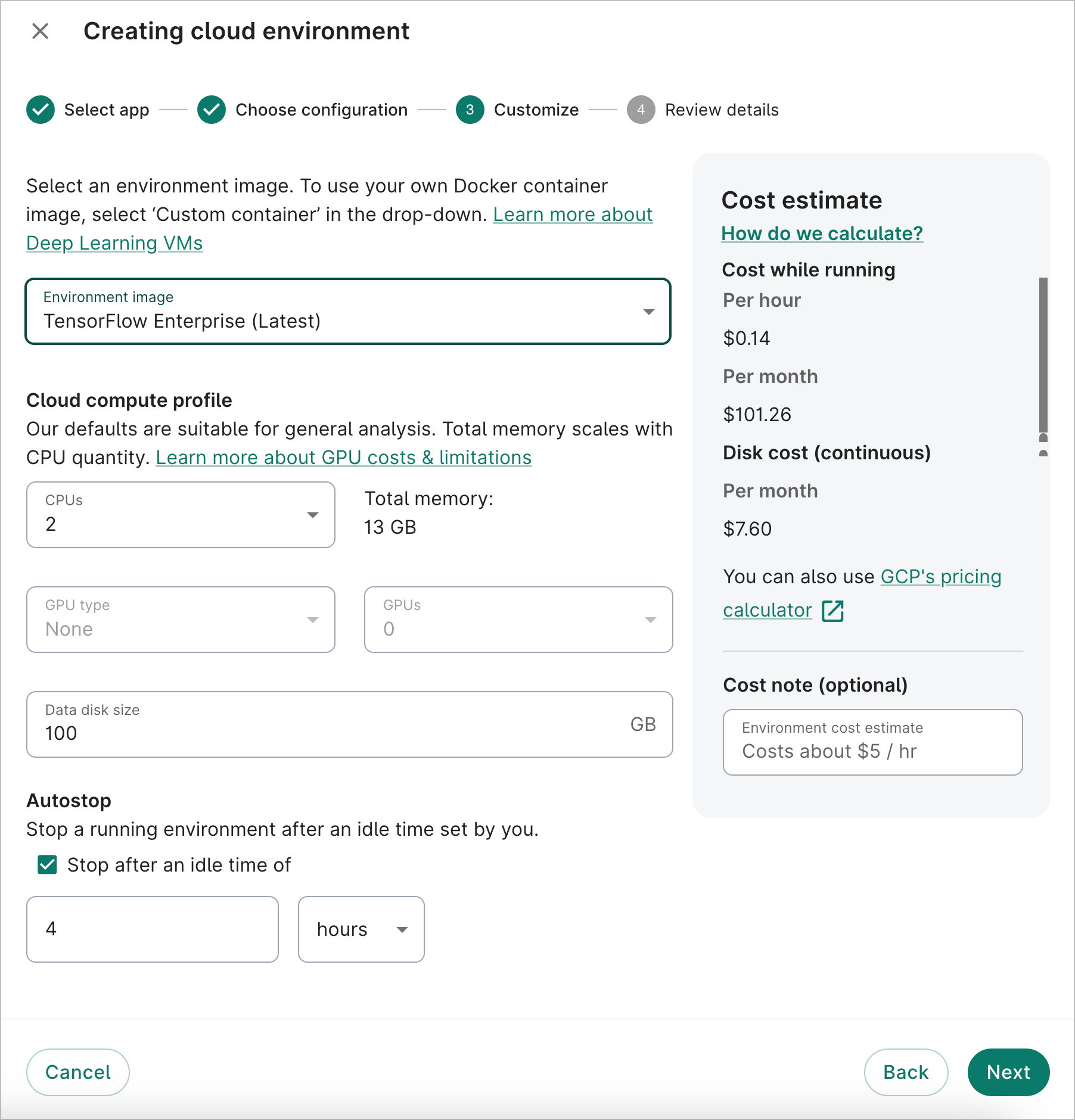
To learn more about configuring the compute profile of your app, see Compute profile configuration options.
Once you've finished customizing configurations, click the Next button.
Be aware
Use of GPUs is subject to certain constraints and has important implications for cost. Please familiarize yourself with them by reading the documentation on Compute profile configuration options before using GPUs in your work.-
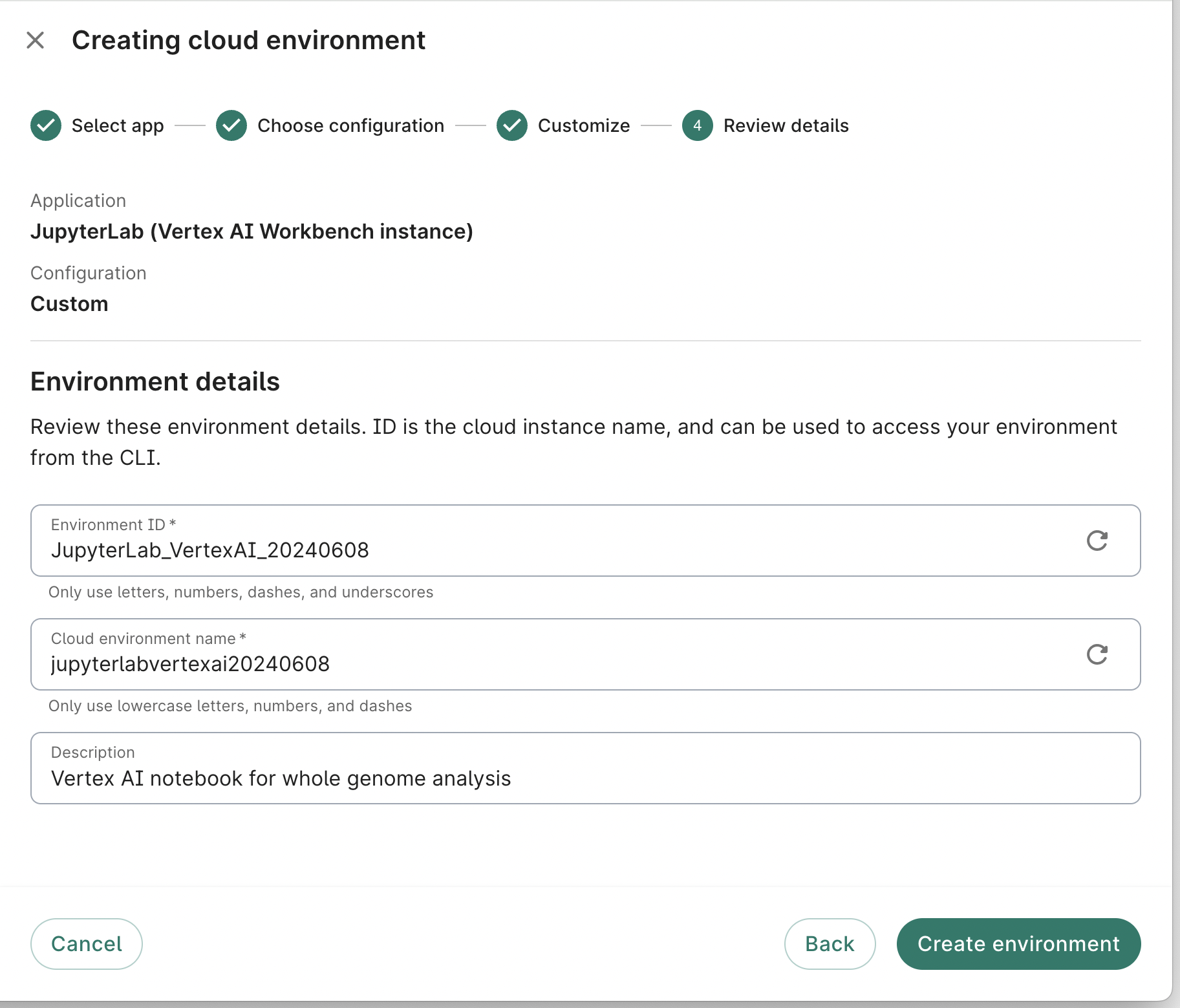
Enter an app ID, name, and optional description. Click the Create app button.
Other app options
Other app options besides JupyterLab Vertex AI Workbench include:
- JupyterLab Spark cluster (Dataproc cluster)
- R Analysis Environment
- Visual Studio Code
- Custom
See Cloud app options for more details.
Operations on existing apps
Edit app ID and description
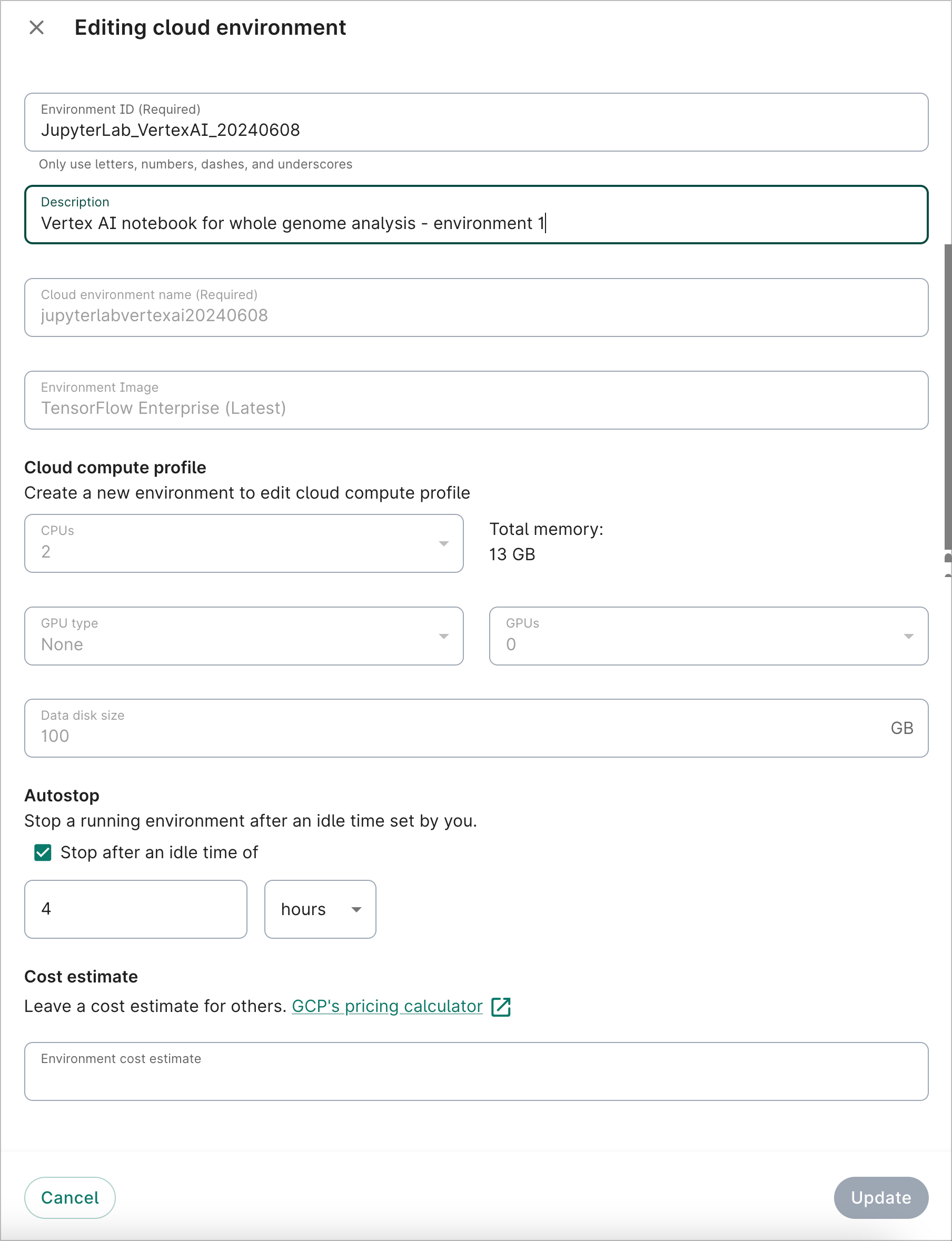
You can edit the ID, description, and autostop idle time of your app at any time. To do so, select Edit in the action menu of the app card. This will bring up the editing dialog. Edit the fields as needed, then click on the Update button to save your changes.
Note
You can also add autostop via the editing dialog to an app that doesn’t already have autostop enabled.Be aware
You cannot edit the name of your app.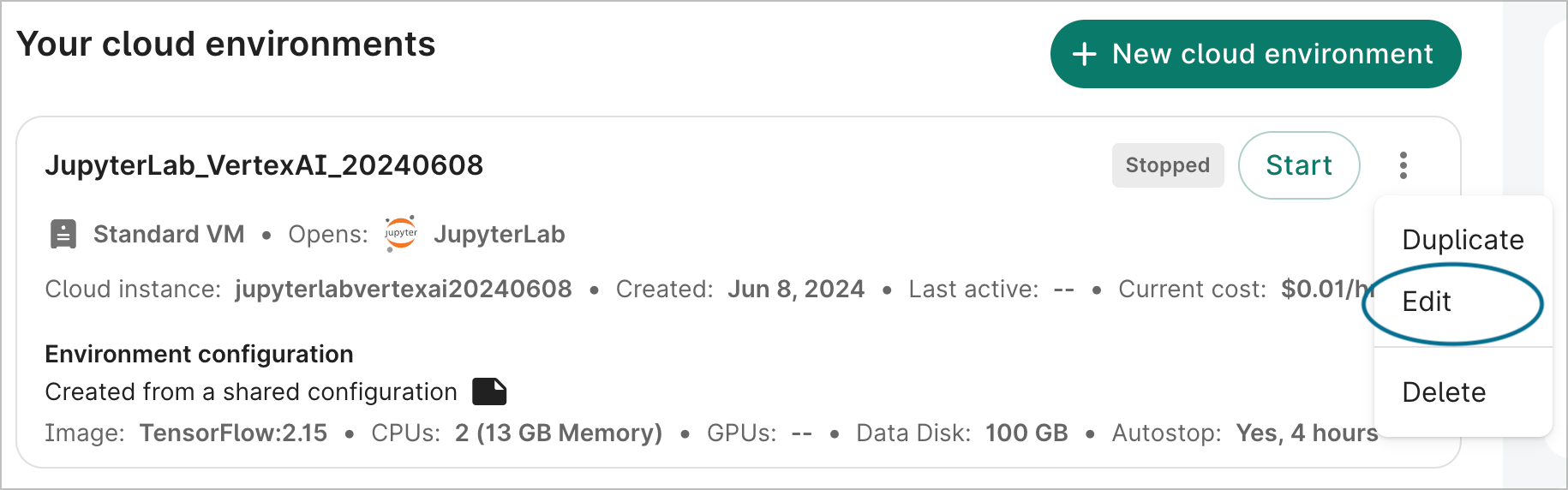
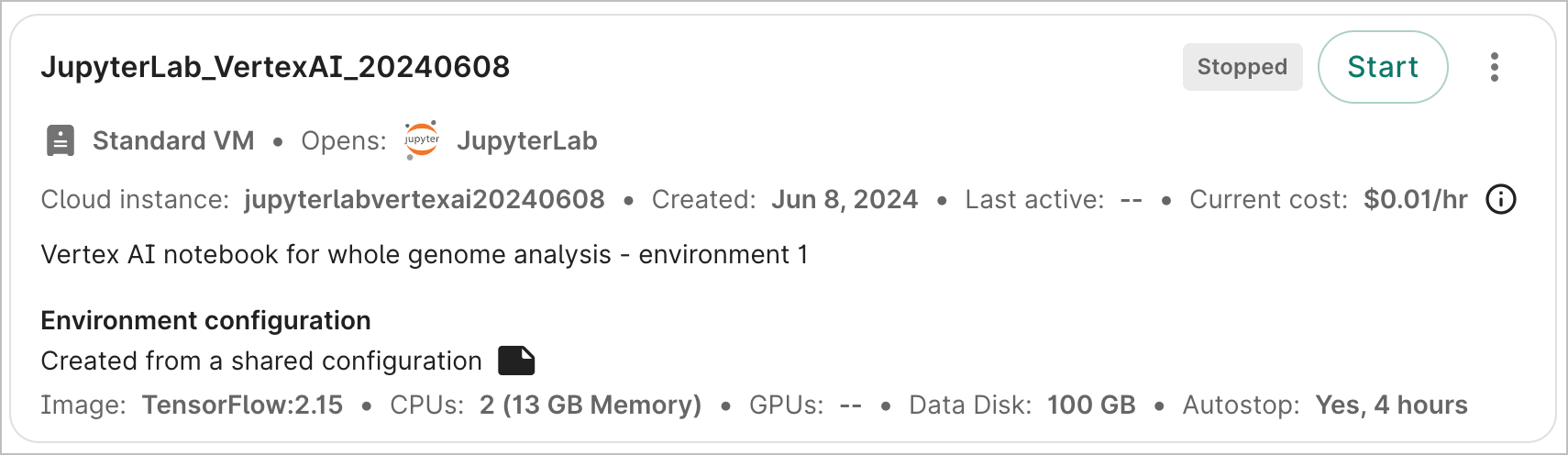
Start an app
To start an app that is currently stopped, click the Start button. This will immediately send the instruction to start the app; there is no confirmation step. However, there may be a lag of a few seconds before the status is updated in the graphical user interface.
Starting the app should take less than a minute. During that time, you cannot stop the app; you can only edit its name and description, duplicate it, or delete it.
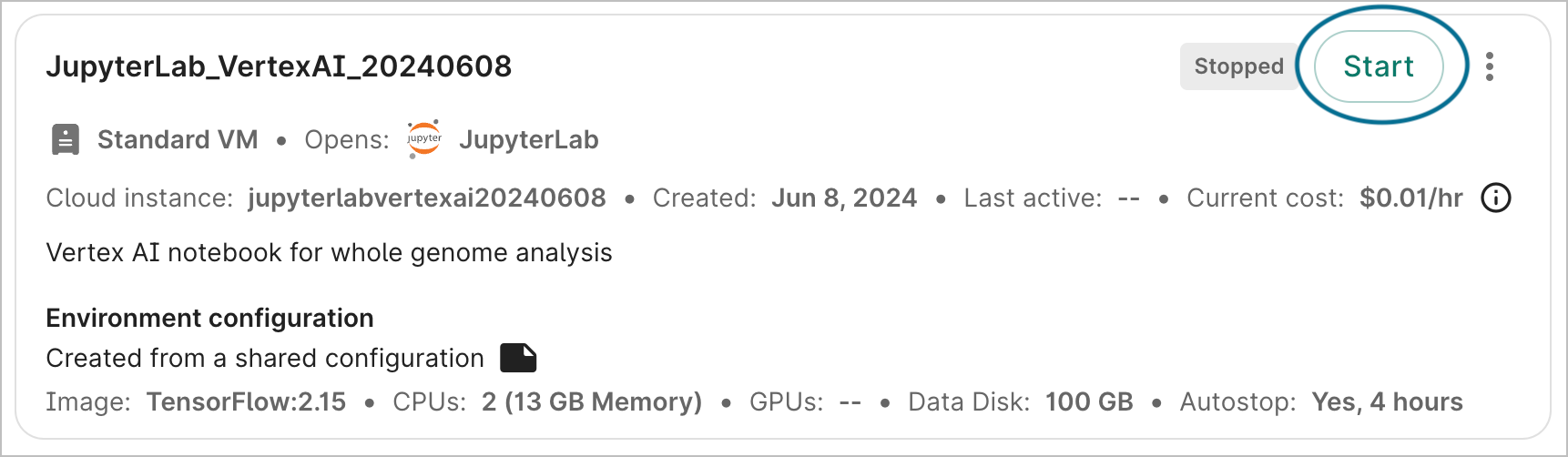
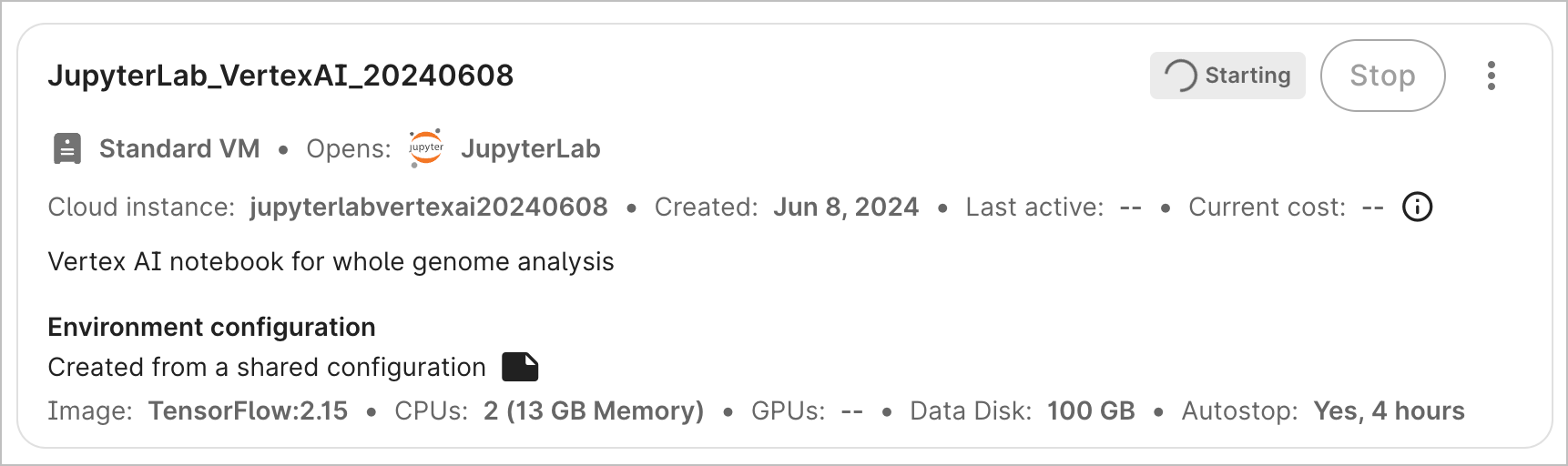
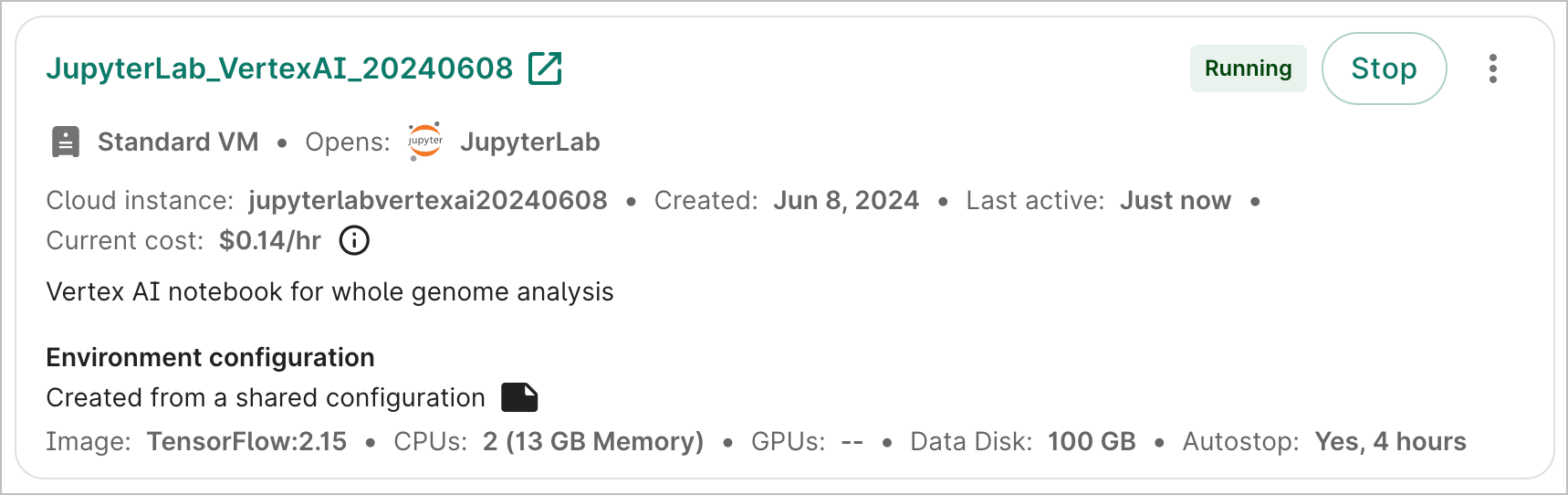
Stop an app
To stop an app that is currently running, click the Stop button. This will immediately send the instruction to stop the app; there is no confirmation step. However, there may be a lag of a few seconds before the status is updated in the graphical user interface.
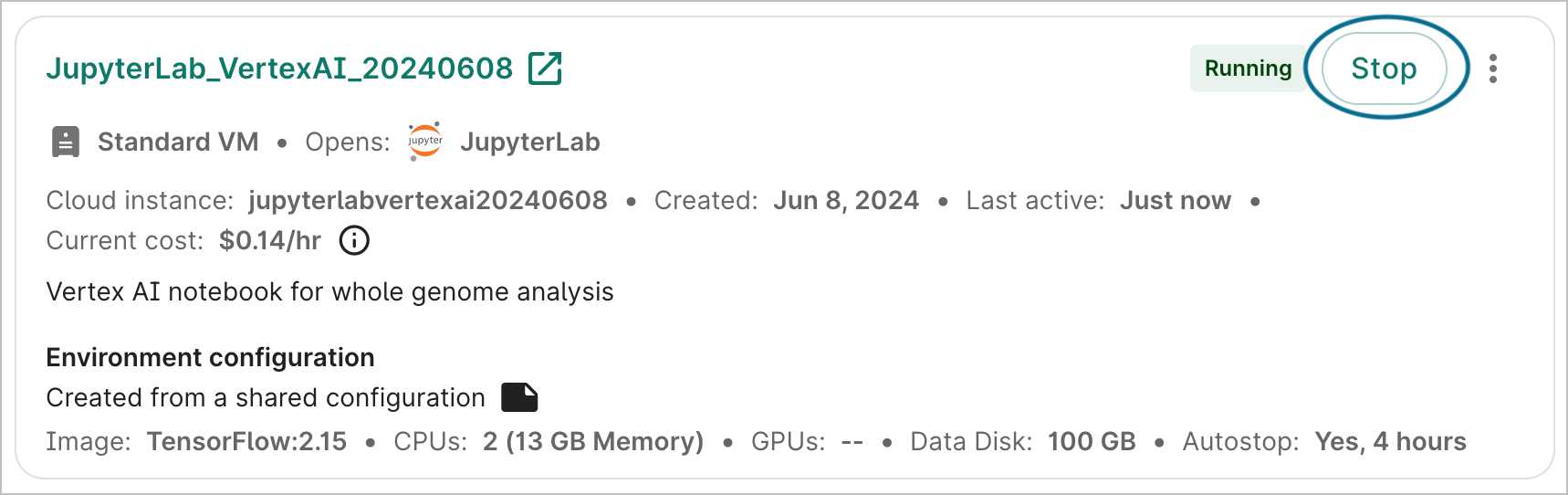
Stopping the app should take less than a minute. During that time, you cannot restart the app; you can only edit its name and description, duplicate it, or delete it.
If your app has autostop enabled, you'll see the autostop idle time listed in the app's card. You can still manually stop the app any time before it’s set to automatically stop.
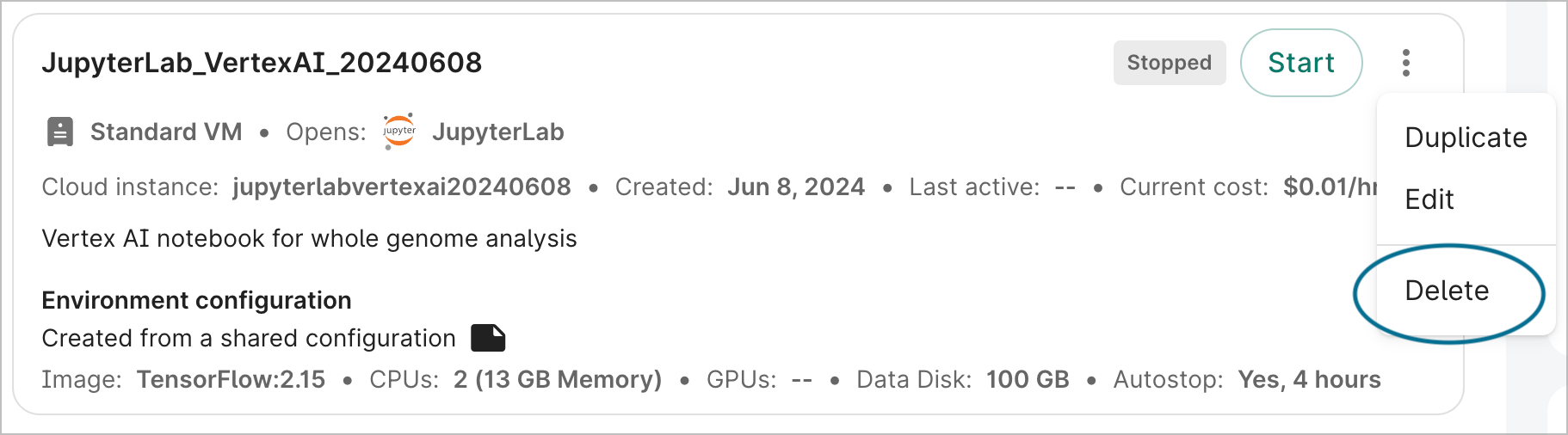
Delete an app
You can delete an app by selecting Delete in the action menu of the app card.
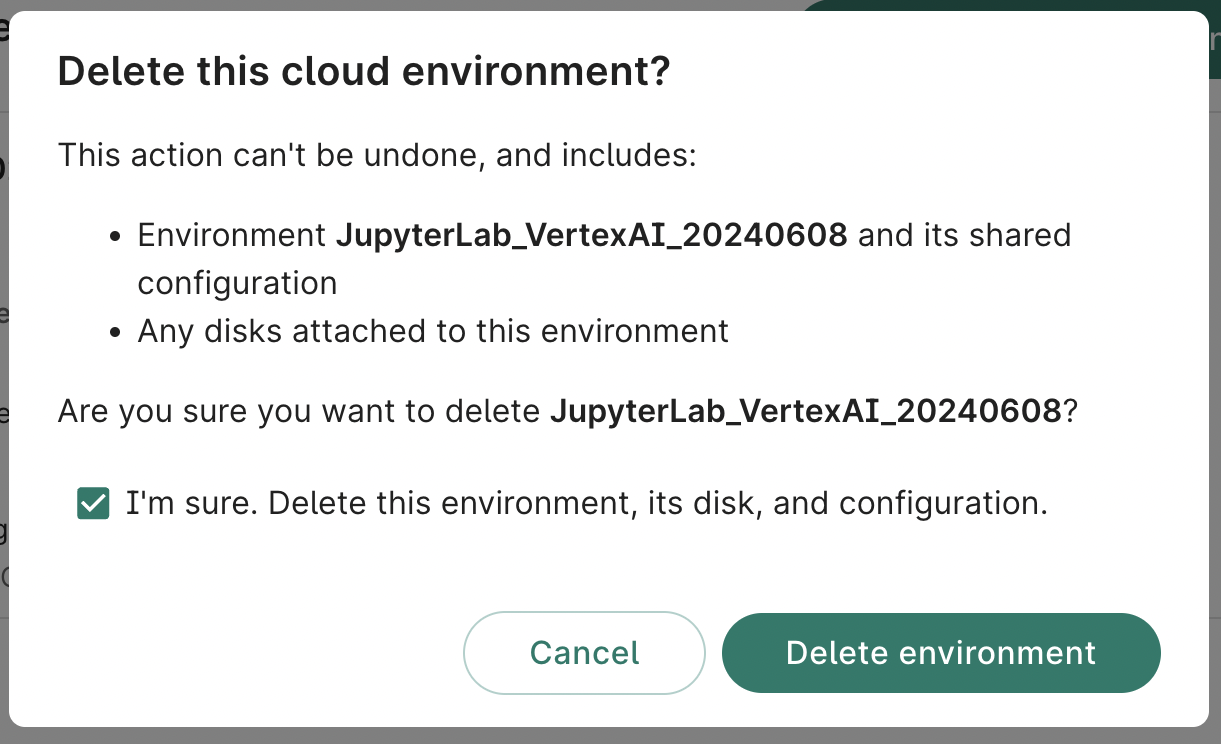
This will bring up a deletion dialog that details what will be deleted and asks you to confirm the deletion request.
To proceed with deletion, check the box confirming your intent to delete the app and its associated resources, then click the Delete app button.
Modify compute profile
You cannot change the app image and cloud compute profile of an existing app through the web UI. To generate a different configuration exclusively through the web UI, you must create a new app with the desired configuration. You can create as many apps as you want within the same workspace.
However, it's possible to modify an existing app's compute profile through the Google Cloud console or via the Workbench CLI (command-line interface), using the wb resource update gcp-notebook command. To do this, the app needs to be STOPPED first, as described in Stop an app.
Note that you can stop and start your apps from the Google Cloud console UI itself.
To modify the compute profile of an existing app through the Google Cloud console:
-
From the right-hand Workspace details panel of the workspace's Overview page, click on the link for your workspace's associated Google Project. This will take you to the Google Cloud console with the correct project set.
-
From the menu in the upper left of the Console, navigate to the
Vertex AIapp page and click onWorkbenchin the left-hand menu (underNOTEBOOKS). If you have a hard time findingVertex AIin the list of Google Cloud apps, you can use the search bar at the top of the console page to search for it.Your app should be listed under the tab labeled
USER-MANAGED NOTEBOOKS(not underINSTANCES). -
Make sure that the app you want to reconfigure is stopped before you try to modify it. Then click on the link for the app to view its details, and click on the
HARDWAREtab: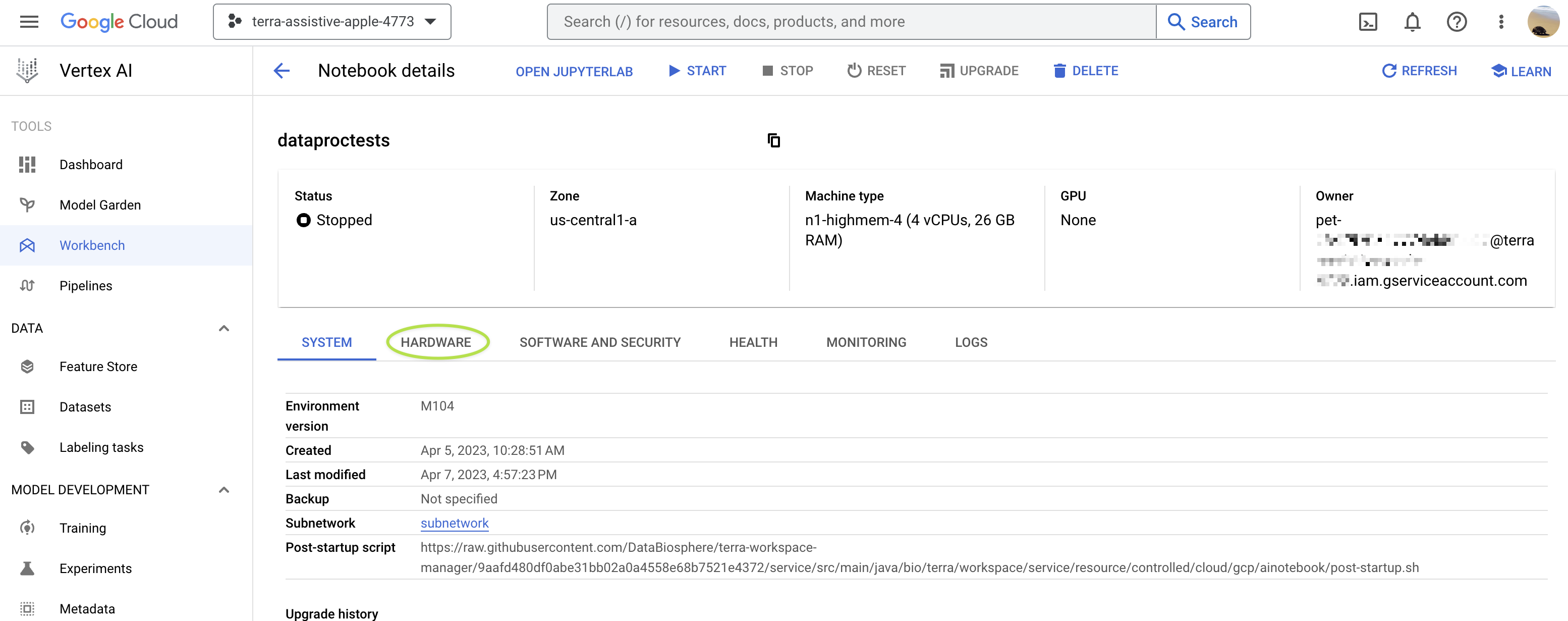
-
Then, update the
machine typeand (optionally)GPUconfiguration settings to the desired values and click SUBMIT. This video walks through the process:
To learn more about the available options, see Compute profile configuration options.
Get cost estimates for different app VM configurations
As you can see in the screencast above, the app cost estimates change as
you reconfigure the machine type and GPU settings. You can use this Cloud console view of your
app to see an estimate of how much your app would cost you if you left it RUNNING
for a month.
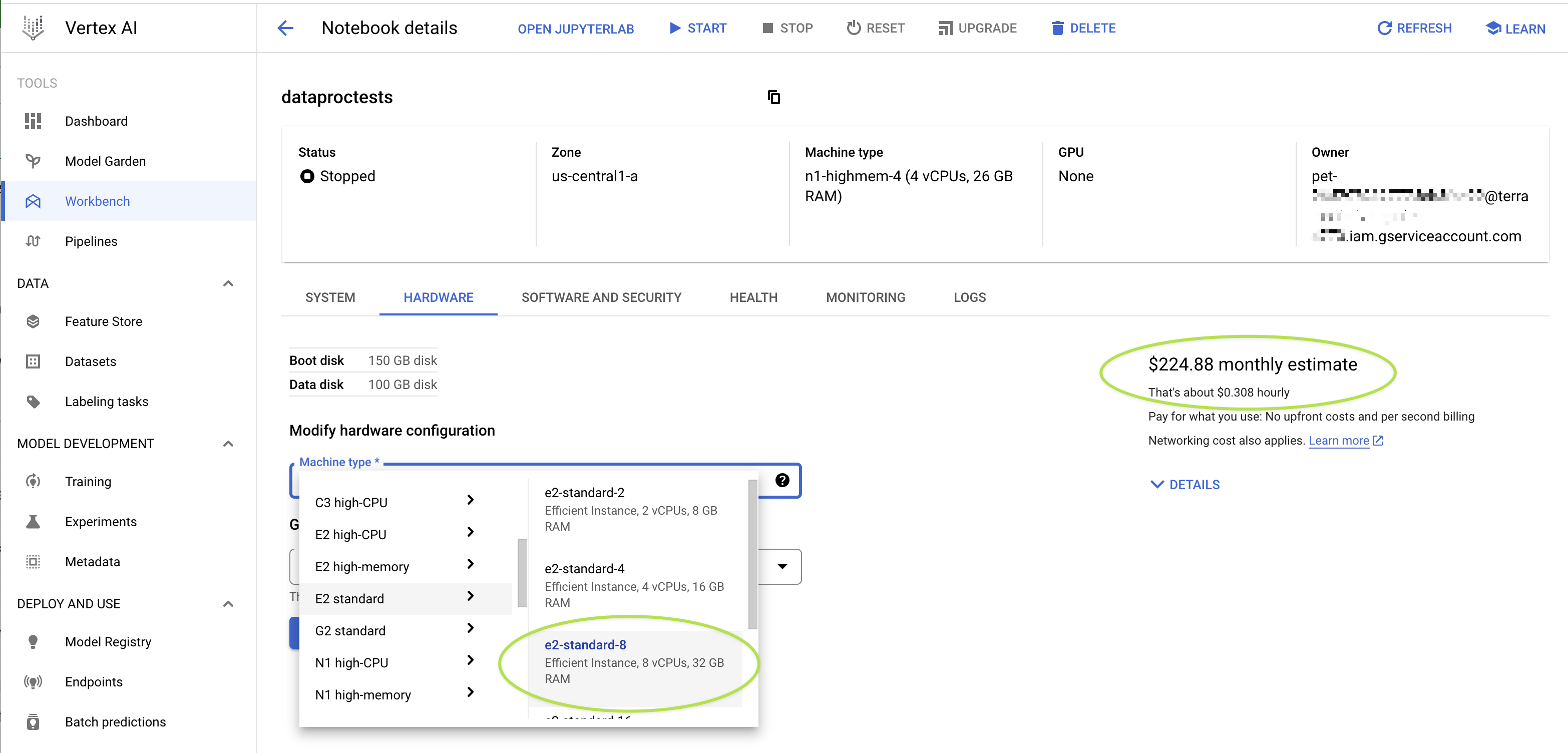
Note that the estimated charges are specifically for a running app; if you stop an app, you are still charged for your app's disk, but you're not incurring compute costs. As discussed above, it's therefore recommended to stop your app when it's not in use.
Note on button locations
On the Apps page, the buttons for operations that apply to existing apps are located in the additional actions menu, which is represented by a "three-dot" icon in the top right corner of each app's card.
Last Modified: 11 December 2024